Introduction: Understanding the Importance of Magnesium
Magnesium is one of the most vital minerals for human health, involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body. From regulating muscle function and blood sugar levels to promoting mental calmness and healthy bones, this mineral plays a major role in maintaining overall wellness.
But when it comes to supplementation, choosing the right form of magnesium is critical. Two of the most popular types are magnesium glycinate and magnesium citrate.
In this article, we’ll compare magnesium glycinate vs citrate, diving deep into their benefits, bioavailability, side effects, uses, and which one is best for specific health conditions.
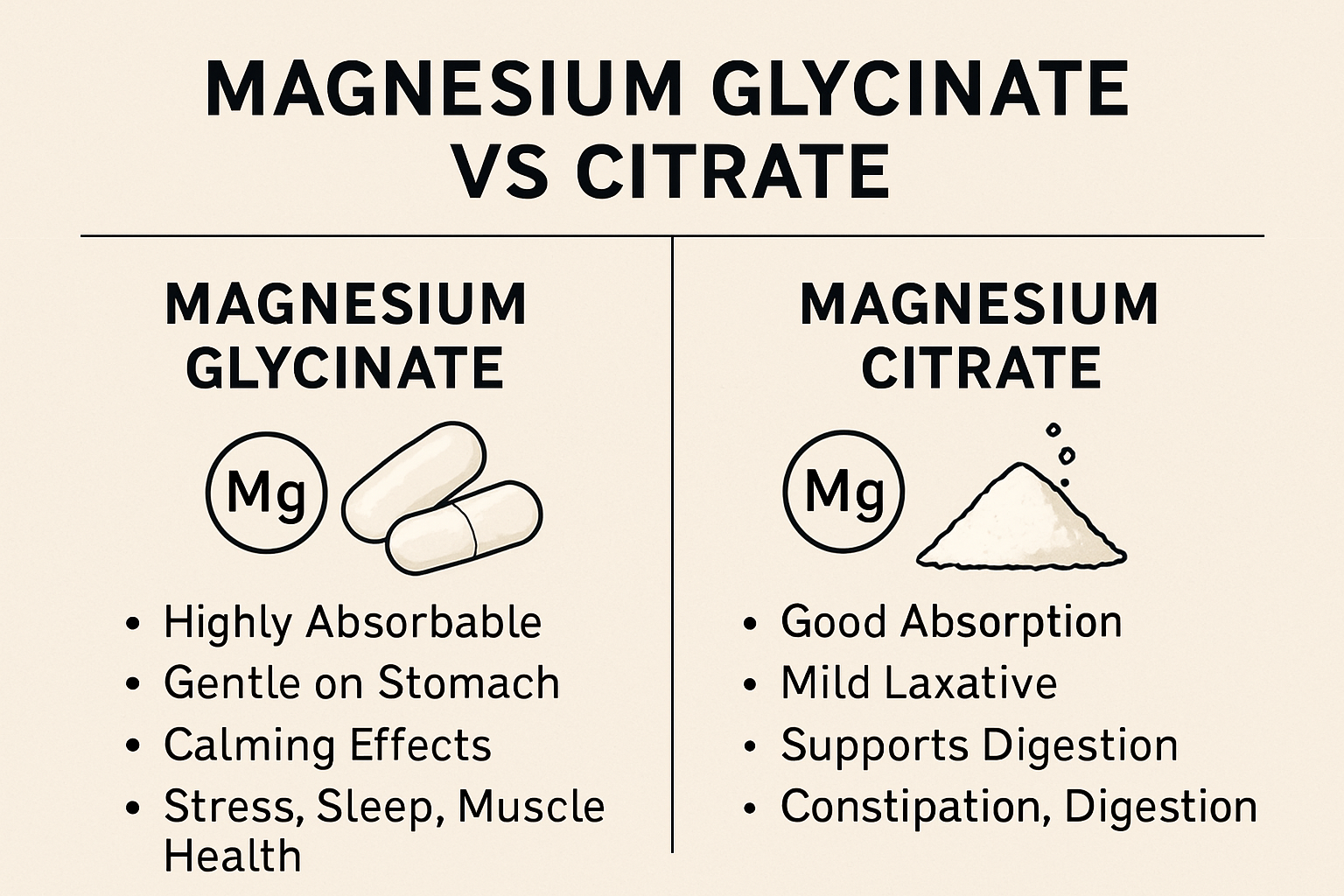
What Is Magnesium Glycinate?
Magnesium glycinate is a compound made by combining magnesium with glycine, an amino acid. This form is known for its high bioavailability and gentle effect on the stomach.
Key Features of Magnesium Glycinate:
- Highly absorbable
- Less likely to cause diarrhea
- Calming effects due to glycine
- Best for stress, anxiety, sleep, and muscle relaxation
What Is Magnesium Citrate?
Magnesium citrate is formed by combining magnesium with citric acid, a natural substance found in citrus fruits. It is also well-absorbed but is commonly used for constipation relief and digestive health.
Key Features of Magnesium Citrate:
- Good absorption rate
- Acts as a mild laxative
- Supports energy production
- Often used in colon cleanses before medical procedures
Magnesium Glycinate vs Citrate: Key Differences
| Feature | Magnesium Glycinate | Magnesium Citrate |
|---|---|---|
| Absorption | Excellent | Good |
| Main Use | Stress, sleep, muscle health | Constipation, digestion |
| Laxative Effect | Rare | Common |
| Calming Effect | Strong (due to glycine) | Mild |
| Digestive Tolerance | Gentle | May cause loose stools |
| Bioavailability | Very high | High |
| Best Time to Take | Evening or bedtime | Morning or empty stomach |
Benefits of Magnesium Glycinate
1. Promotes Relaxation and Sleep
Magnesium glycinate is often recommended for insomnia and anxiety because glycine is a calming amino acid that promotes deep, restful sleep.
2. Reduces Anxiety and Stress
Magnesium regulates the nervous system and helps prevent overstimulation. Combined with glycine, it acts as a natural anxiolytic.
3. Muscle Support
It helps in relaxing muscles, reducing cramps, and is often used by athletes for post-workout recovery.
4. Gentle on Stomach
Unlike citrate, magnesium glycinate does not typically cause diarrhea, making it ideal for people with sensitive digestive systems.
Benefits of Magnesium Citrate
1. Relieves Constipation
Magnesium citrate is an osmotic laxative, drawing water into the intestines and stimulating bowel movements. It is commonly used for short-term constipation relief.
2. Supports Digestive Cleansing
Doctors often prescribe magnesium citrate before procedures like colonoscopies because it effectively cleans out the colon.
3. Energy Production
Magnesium citrate plays a role in ATP production, the body’s energy currency, helping fight fatigue.
Who Should Take Magnesium Glycinate?
Magnesium glycinate is ideal for individuals who:
- Experience anxiety or panic attacks
- Struggle with insomnia or poor sleep quality
- Suffer from muscle cramps or twitching
- Have sensitive stomachs
- Are long-term supplement users who require daily magnesium
Who Should Take Magnesium Citrate?
Magnesium citrate is best suited for people who:
- Are constipated or have irregular bowel movements
- Need a short-term cleanse or detox
- Want to improve digestive motility
- Are looking for general magnesium support
Magnesium Glycinate vs Citrate for Specific Health Conditions
1. For Sleep and Anxiety
Winner: Magnesium Glycinate
Its calming effect on the nervous system makes it superior for relaxation and stress management.
2. For Constipation
Winner: Magnesium Citrate
Due to its laxative properties, magnesium citrate is effective for relieving occasional constipation.
3. For Muscle Cramps
Winner: Magnesium Glycinate
Its ability to relax muscles and prevent twitching makes it the better choice for muscle-related issues.
4. For Daily Magnesium Maintenance
Winner: Magnesium Glycinate
Its digestive tolerance and bioavailability make it suitable for long-term use.
5. For Digestive Cleansing
Winner: Magnesium Citrate
Used in pre-colonoscopy protocols, magnesium citrate is excellent for thorough colon cleansing.
Bioavailability: Which One Is Absorbed Better?
While both magnesium glycinate and citrate are well-absorbed, glycinate has a slight edge due to:
- Chelation with glycine
- Higher retention in body tissues
- Lower chance of being flushed out with stools
This makes magnesium glycinate a preferred option for those with magnesium deficiency.
Side Effects of Magnesium Glycinate and Citrate
Magnesium Glycinate Side Effects:
- Rare, but may include:
- Drowsiness
- Low blood pressure (in very high doses)
- Drug interactions (e.g., antibiotics, diuretics)
Magnesium Citrate Side Effects:
- More common due to its laxative nature:
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramping
- Electrolyte imbalance (if overused)
- Dehydration
Important: Always consult a doctor before starting any new supplement.
Dosage and How to Take
Recommended Daily Magnesium Intake (RDI):
| Age & Gender | RDI |
|---|---|
| Adult men | 400–420 mg |
| Adult women | 310–320 mg |
| Pregnant women | 350–360 mg |
Typical Supplement Dosage:
- Magnesium glycinate: 100–400 mg/day (divided doses)
- Magnesium citrate: 200–500 mg/day (depending on laxative needs)
Tip: Take magnesium glycinate with meals or at night. Take citrate on an empty stomach if using for constipation.
Natural Food Sources of Magnesium
While supplements help, don’t forget to include magnesium-rich foods:
- Dark leafy greens (spinach, kale)
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, pumpkin seeds)
- Whole grains
- Legumes
- Avocados
- Dark chocolate
- Bananas
Can You Take Magnesium Glycinate and Citrate Together?
Yes, but only under medical supervision.
Some people combine them to get the calming benefits of glycinate and the digestive support from citrate, but careful monitoring of total magnesium intake is crucial to avoid side effects like diarrhea or low blood pressure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is magnesium glycinate better than citrate?
It depends on your health goal. For sleep and anxiety, glycinate is better. For constipation, citrate is preferred.
2. Does magnesium citrate help with anxiety?
It can help, but not as effectively as magnesium glycinate, which is more calming due to its glycine content.
3. Is magnesium glycinate good for long-term use?
Yes, it’s gentle and well-tolerated, making it a good choice for ongoing supplementation.
4. Can I switch between the two?
Yes, many people try different forms to see what works best for them. However, always follow proper dosing instructions.
5. Which form has fewer side effects?
Magnesium glycinate typically has fewer digestive side effects compared to magnesium citrate.
Final Verdict: Magnesium Glycinate vs Citrate – Which Should You Choose?
| Goal | Best Form |
|---|---|
| Better Sleep | Magnesium Glycinate |
| Stress and Anxiety Relief | Magnesium Glycinate |
| Constipation Relief | Magnesium Citrate |
| Daily Supplementation | Magnesium Glycinate |
| Short-Term Colon Cleanse | Magnesium Citrate |
If you’re still unsure, start with magnesium glycinate for overall wellness and see how your body responds. For specific digestive issues, magnesium citrate can be added short-term under guidance.
Conclusion
When choosing between magnesium glycinate vs citrate, there is no one-size-fits-all answer. Your health condition, goals, and body response should guide your choice.
Whether you’re aiming to sleep better, manage stress, or relieve constipation, understanding the unique benefits of each form can help you make an informed decision.
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement routine.